Java Naming Conventions
Estimated time to read: 1 minute
Overview¶
- Names are used to denote classes, objects, attributes and methods
- A name is a sequence of letters, number and _'s
- Names may not start with a number
- Java names are case sensitive
Classes¶
Class names utilise Camel Case eg ThisIsAClassNameInCamelCase
Other Names¶
Other names usually start with lower case letters, but are capitalised from there eg setManagerType
Finals / Constants¶
Finals (Constants) are all upper case as a stylistic convention. Underscores are used to separate individual words. eg THIS_IS_A_FINAL
Reserved Words¶
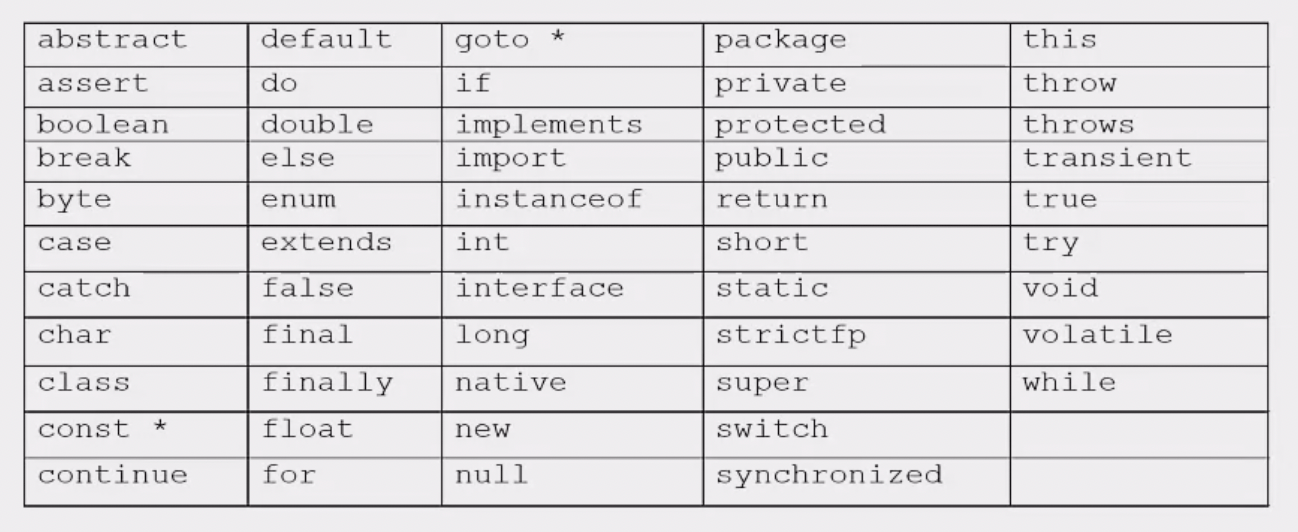
These are Java's keywords, which signal the compiler to perform some internal operations. These can not be used as identifiers.
Comments¶
Single line comments¶
Single line comments start with a //, these can be placed anywhere within the line (unless it is escaped)
public class Car {
//This is a single line comment
private int speed; //This is also a comment, but does not affect the code
}
Multi line comments¶
Multi line comments start with /* and end with a */.
However, if a multi line comment starts with /** instead of /*, the contents of the comment wil be included in the documentation generated by javadoc.