Four Design Principles
Estimated time to read: 1 minute
In order for a system to be object oriented, it should adhere to certain design principles.
These design principles are:
| Principle | Goal | Terms | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abstraction | To reduce complexity by only showing relevant information | abstract class abstract method extend | |
| Decomposition | To reduce complexity by separating problems | association aggregation composition | |
| Encapsulation | To restrict access to data to protect them and reduce complexity | getter setter private protected public | |
| Generalisation (Polymorphism/Inheritance) | To reduce complexity by having an umbrella term | superclass subclass interface implements extends |
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Decomposition (Breaking objects down)
- Generalisation (Polymorphism)
Object-Oriented Programming System¶
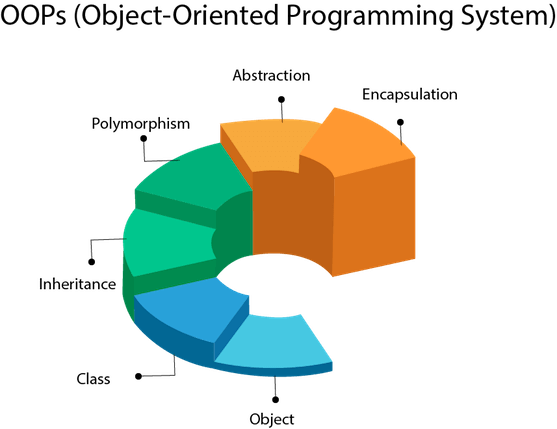
Object-oriented programming refers to the concept in high-level languages such as Java and Python that uses Objects and classes in their implementations. OOP has four major building blocks which are, Polymorphism, Encapsulation, Abstraction, and Inheritance.
There are other programming paradigms such as Procedural programming in which codes are written in sequentially. Python and Java are multi-paradigm high-level programming languages that means they support both OOP and procedural programming.